NetPicker.io
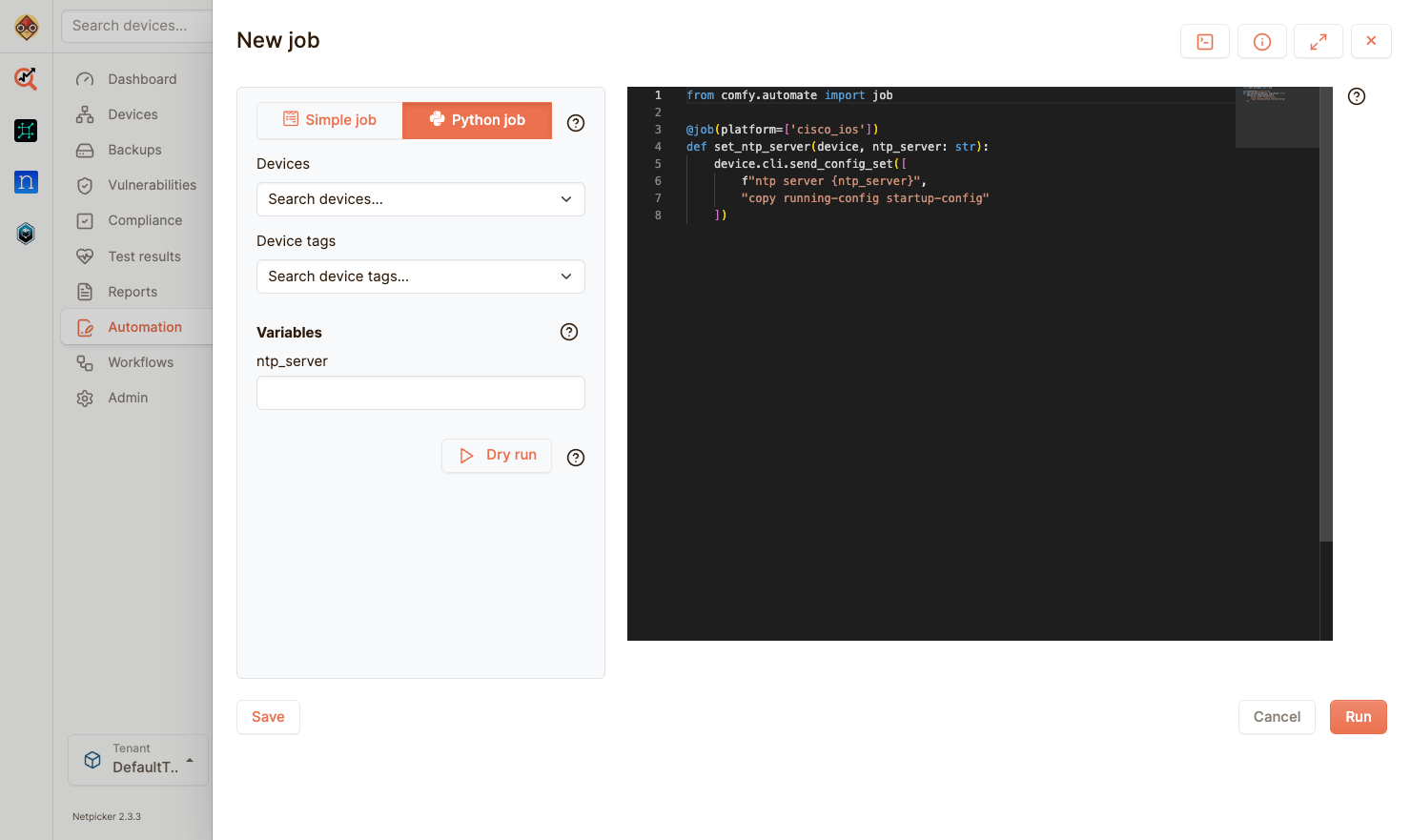
NetPicker.io is a network discovery and inventory management platform designed specifically for network automation and NetDevOps workflows. It provides automated network device discovery, configuration collection, and inventory management to support modern network operations.
Key Features
- Automated Network Discovery: Scan and discover network devices automatically
- Configuration Collection: Gather device configurations and settings
- Inventory Management: Centralized network device inventory
- API Integration: RESTful APIs for automation workflows
- Real-time Monitoring: Live device status and health monitoring
- Multi-vendor Support: Works with Cisco, Juniper, Arista, and other vendors
- Cloud-native Architecture: Scalable and modern platform design
Typical Use Cases
- Network Inventory Automation: Automatically discover and catalog network devices
- Configuration Management: Collect and track device configurations
- Network Documentation: Generate up-to-date network documentation
- Automation Workflows: Integrate with Ansible, Terraform, and other automation tools
- Compliance Auditing: Track device configurations for compliance requirements
- Network Mapping: Visualize network topology and device relationships
Getting Started
1. Sign Up and Setup
- Visit netpicker.io
- Create an account and verify your email
- Complete the initial setup wizard
- Configure your network scanning parameters
Deployment Options
NetPicker.io offers multiple deployment options to suit different environments and requirements:
Cloud Deployment (SaaS)
- Quick Start: Sign up at netpicker.io for immediate access
- Managed Service: Fully managed by NetPicker.io team
- Automatic Updates: Always running the latest version
- Scalability: Handles growing network environments automatically
On-Premise Deployment
NetPicker.io can be deployed on your own infrastructure for enhanced security and control:
Docker Deployment
# docker-compose.yml
version: '3.8'
services:
netpicker:
image: netpicker/netpicker:latest
container_name: netpicker
ports:
- "8080:8080"
environment:
- NP_DATABASE_URL=postgresql://user:password@db:5432/netpicker
- NP_REDIS_URL=redis://redis:6379
- NP_SECRET_KEY=your-secret-key
volumes:
- netpicker_data:/app/data
- netpicker_logs:/app/logs
depends_on:
- db
- redis
db:
image: postgres:13
container_name: netpicker-db
environment:
- POSTGRES_DB=netpicker
- POSTGRES_USER=user
- POSTGRES_PASSWORD=password
volumes:
- postgres_data:/var/lib/postgresql/data
redis:
image: redis:6-alpine
container_name: netpicker-redis
volumes:
- redis_data:/data
volumes:
netpicker_data:
netpicker_logs:
postgres_data:
redis_data:
Terraform Deployment
# main.tf
terraform {
required_providers {
docker = {
source = "kreuzwerker/docker"
version = "~> 3.0"
}
}
}
resource "docker_network" "netpicker_network" {
name = "netpicker-network"
}
resource "docker_volume" "netpicker_data" {
name = "netpicker-data"
}
resource "docker_volume" "postgres_data" {
name = "postgres-data"
}
resource "docker_container" "netpicker_db" {
name = "netpicker-db"
image = "postgres:13"
networks_advanced {
name = docker_network.netpicker_network.name
}
volumes {
volume_name = docker_volume.postgres_data.name
container_path = "/var/lib/postgresql/data"
}
env = [
"POSTGRES_DB=netpicker",
"POSTGRES_USER=netpicker",
"POSTGRES_PASSWORD=${var.db_password}"
]
}
resource "docker_container" "netpicker" {
name = "netpicker"
image = "netpicker/netpicker:latest"
networks_advanced {
name = docker_network.netpicker_network.name
}
volumes {
volume_name = docker_volume.netpicker_data.name
container_path = "/app/data"
}
ports {
internal = 8080
external = 8080
}
env = [
"NP_DATABASE_URL=postgresql://netpicker:${var.db_password}@netpicker-db:5432/netpicker",
"NP_SECRET_KEY=${var.secret_key}"
]
depends_on = [docker_container.netpicker_db]
}
# variables.tf
variable "db_password" {
description = "Database password"
type = string
sensitive = true
}
variable "secret_key" {
description = "NetPicker secret key"
type = string
sensitive = true
}
Kubernetes Deployment
# netpicker-deployment.yaml
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: netpicker
spec:
replicas: 1
selector:
matchLabels:
app: netpicker
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: netpicker
spec:
containers:
- name: netpicker
image: netpicker/netpicker:latest
ports:
- containerPort: 8080
env:
- name: NP_DATABASE_URL
valueFrom:
secretKeyRef:
name: netpicker-secrets
key: database-url
- name: NP_SECRET_KEY
valueFrom:
secretKeyRef:
name: netpicker-secrets
key: secret-key
volumeMounts:
- name: netpicker-data
mountPath: /app/data
volumes:
- name: netpicker-data
persistentVolumeClaim:
claimName: netpicker-pvc
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: netpicker-service
spec:
selector:
app: netpicker
ports:
- port: 80
targetPort: 8080
type: LoadBalancer
Deployment Considerations
Cloud vs On-Premise
- Cloud: Faster setup, managed updates, no infrastructure maintenance
- On-Premise: Full control, data sovereignty, custom integrations
Resource Requirements
- Minimum: 2 CPU cores, 4GB RAM, 20GB storage
- Recommended: 4 CPU cores, 8GB RAM, 100GB storage
- Database: PostgreSQL 12+ or MySQL 8+
- Cache: Redis 6+ (optional but recommended)
Security Considerations
- Use HTTPS in production
- Implement proper authentication and authorization
- Secure database connections
- Regular security updates
- Network segmentation for sensitive environments
2. Network Discovery
- Add Network Ranges: Define IP ranges to scan
- Configure Credentials: Add device access credentials
- Start Discovery: Initiate automated network scanning
- Review Results: Verify discovered devices and configurations
3. API Integration
# Example API call to get device inventory
curl -X GET "https://api.netpicker.io/v1/devices" \
-H "Authorization: Bearer YOUR_API_TOKEN" \
-H "Content-Type: application/json"
4. Automation Integration
# Example Ansible integration
- name: Get device inventory from NetPicker
uri:
url: "https://api.netpicker.io/v1/devices"
method: GET
headers:
Authorization: "Bearer {{ netpicker_api_token }}"
return_content: yes
register: netpicker_devices
Integration Examples
Ansible Integration
# Use NetPicker as dynamic inventory source
- name: Configure network devices from NetPicker inventory
hosts: "{{ groups['network_devices'] }}"
gather_facts: no
tasks:
- name: Get device configuration
uri:
url: "https://api.netpicker.io/v1/devices/{{ inventory_hostname }}/config"
method: GET
headers:
Authorization: "Bearer {{ netpicker_api_token }}"
register: device_config
Terraform Integration
# Use NetPicker data source for infrastructure management
data "external" "netpicker_devices" {
program = ["curl", "-s", "-H", "Authorization: Bearer ${var.netpicker_token}",
"https://api.netpicker.io/v1/devices"]
}
resource "aws_instance" "network_monitor" {
count = length(data.external.netpicker_devices.result.devices)
# ... instance configuration
}
Best Practices
1. Credential Management
- Use secure credential storage
- Implement role-based access control
- Rotate credentials regularly
- Use API tokens for automation
2. Network Scanning
- Schedule scans during maintenance windows
- Use appropriate scan intervals
- Monitor scan performance and resource usage
- Validate discovered devices
3. Data Management
- Regular backups of inventory data
- Version control for configuration changes
- Data retention policies
- Compliance with data protection regulations
4. Integration Strategy
- Start with basic discovery and inventory
- Gradually add automation workflows
- Implement monitoring and alerting
- Build custom integrations as needed
Resources
For more on network automation tools, see the NetDevOps Tools Index.